Features
- Hot water temperature control
- Heating temperature control
- Smart heating temperature control modes:
- PID
- Equithermic curves - adjusts the temperature based on indoor and outdoor temperatures
- Hysteresis setting (for accurate maintenance of room temperature)
- Ability to connect an external sensor to monitor outdoor temperature (DS18B20)
- Diagnostics:
- The process of heating the coolant for heating: works / does not work
- The process of heating water for hot water: working / not working
- Display of boiler errors
- Burner status: on/off
- Burner modulation level in percent
- Pressure in the heating system
- Gateway status (depending on errors and connection status)
- Boiler connection status via OpenTherm interface
- The current temperature of the heat carrier (usually the return heat carrier)
- Set coolant temperature (depending on the selected mode)
- Current hot water temperature
- Auto tuning of PID and Equitherm parameters (in development)
- Home Assistant integration via MQTT. The ability to create any automation for the boiler!
Compatible Open Therm Adapters
- Ihor Melnyk OpenTherm Adapter
- OpenTherm master shield for Wemos/Lolin
- And others. It's just that the adapter must implement the schema
Quick Start
Dependencies
- ArduinoJson
- TelnetStream
- EEManager
- ESP8266Scheduler
- NTPClient
- PubSubClient
- GyverFilters
- MultiMap
- WiFiManager
Settings
- Connect to OpenTherm Gateway hotspot
- Open configuration page in browser: 192.168.4.1
- Set up a connection to your wifi network
- Set up a connection to your MQTT server
After connecting to your wifi network, you can go to the setup page at the address that esp8266 received. The OTGateway device will be automatically added to homeassistant if MQTT server ip, login and password are correct.
HomeAsssistant settings
@todo
About ratios
Equitherm
N - heating curve coefficient. The coefficient is selected individually, depending on the insulation of the room, the heated area, etc.
Range: 0.3...10, default: 0.67, step 0.01
*K - сorrection for desired room temperature.
Range: 0...10, default: 1, step 0.01
T - thermostat correction.
Range: 0...10, default: 5, step 0.01
Instructions for fit coefficients:
- The first thing you need to do is to fit the curve (N coefficient). If your home has low heat loss, then start with 0.5. Otherwise start at 0.7. When the temperature inside the house stops changing, increase or decrease the coefficient value in increments of 0.1 to select the optimal curve.
Please note that passive heating (sun) will affect the house temperature during curve fitting. This process is not fast and will take you 1-2 days. Important. During curve fitting, the temperature must be kept stable as the outside temperature changes. The temperature does not have to be equal to the set one.
For example. You fit curve 0.67; set temperature 23; the temperature in the house is 20 degrees while the outside temperature is -10 degrees and -5 degrees. This is good. - After fitting the curve, you must select the K coefficient. It influences the boiler temperature correction to maintain the set temperature. For example. Set temperature: 23 degrees; temperature in the house: 20 degrees. Try setting it to 5 and see how the temperature in the house changes after stabilization. Select the value so that the temperature in the house is close to the set.
- Now you can choose the T coefficient. Simply put, it affects the sharpness of the temperature change. If you want fast heating, then set a high value (6-10), but then the room may overheat. If you want smooth heating, set 1-5. Choose the optimal value for yourself.
Read more about the algorithm here.
PID
See Wikipedia.
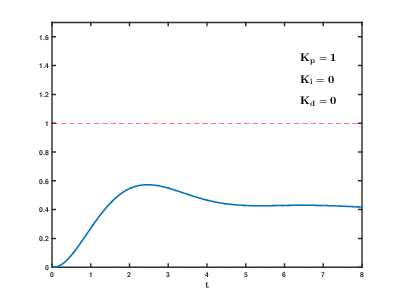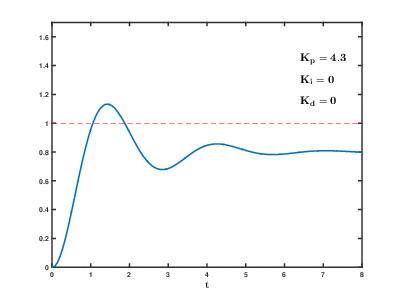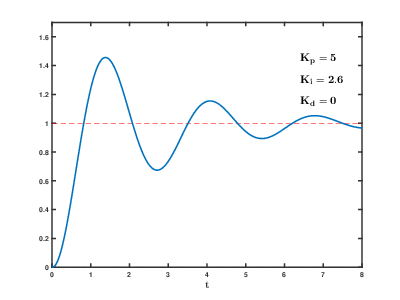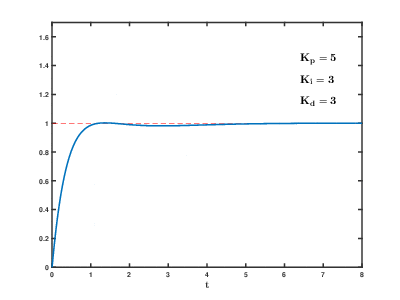
In Google you can find instructions for tuning the PID controller.
Use Equitherm mode + PID mode
@todo
Debug
To display DEBUG messages you must enable debug in settings (switch is disabled by default). You can connect via Telnet to read messages. IP: esp8266 ip, port: 23
